The patient-matched stents are made specifically to fit the patients’ airways
Content is property of Cleveland Clinic and for news media use only.

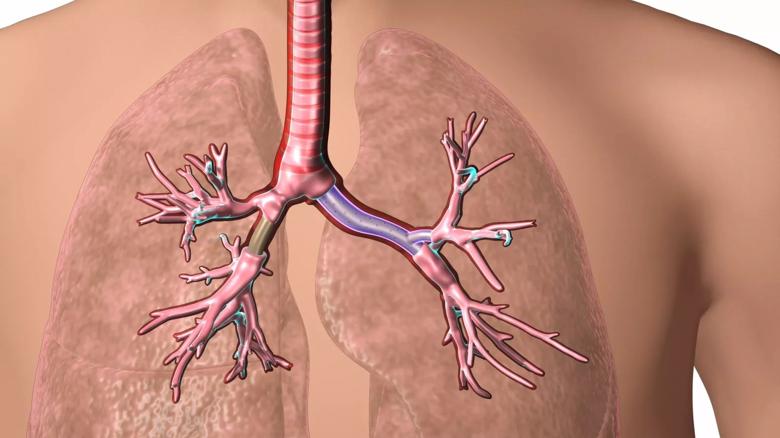
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/0b75847b-2eea-4bd5-8d87-2965a40b02c2/lung-stent-video-Capture_jpg)
Click on the image to view or download a video animation of the 3D patient-specific airway stent developed at Cleveland Clinic.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared patient-specific airway stents developed by Cleveland Clinic physician Tom Gildea, M.D.
The stents are used to keep open the airways of patients with serious breathing disorders, such as those caused by tumors, inflammation, trauma or other masses. Until now, the patient-specific devices were being implanted under FDA’s compassionate use program, which allows patients who have failed all available forms of treatment to receive investigational ones not yet available to the public.
Standard airway stents come in a limited number of sizes and shapes and are generally designed for larger airways. However, no two patient anatomies are alike, making it difficult to get a perfect fit, especially for those with complex conditions. Even in parts of the airways that are easily accessible, ill-fitting standard stents can result in stent kinking and bending as well as airway complications such as growth of new tissue, mucus impaction and tissue death.
The patient-specific stents developed by Dr. Gildea and his engineering team are designed using CT scans and proprietary 3D visualization software. The molds for the stents are then printed using a 3D printer and injected with medical-grade silicone. This process allows them to perfectly fit a patient’s anatomy.

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d59cf2b9-6cb6-4e10-a678-023250f6d481/Gildea_Thomas_579865L_jpg)
Tom Gildea, M.D.
“Breathing is something many people take for granted, but for many of these patients, every breath can be a struggle. It’s been gratifying to see patients receiving the customized stents feeling relief right away.” said Dr. Gildea, section head of bronchoscopy at Cleveland Clinic. “We are excited to be able to bring this technology to more patients across the country and grateful for the patients and donors who have worked with us to help pioneer this technology.”
Another advantage of the patient-specific silicone stents is they have the potential to be more tolerable than traditional silicone stents, which, in certain patients, may have to be frequently changed or cleaned due to problems from a poor fit. In studies, the patient-specific stents lasted, on average, about a year versus 90 days for stock stents. Furthermore, the patient-specific stents exhibited shorter procedure times and improved patient-reported symptoms, leading to a reduced need for stent changes and modifications.
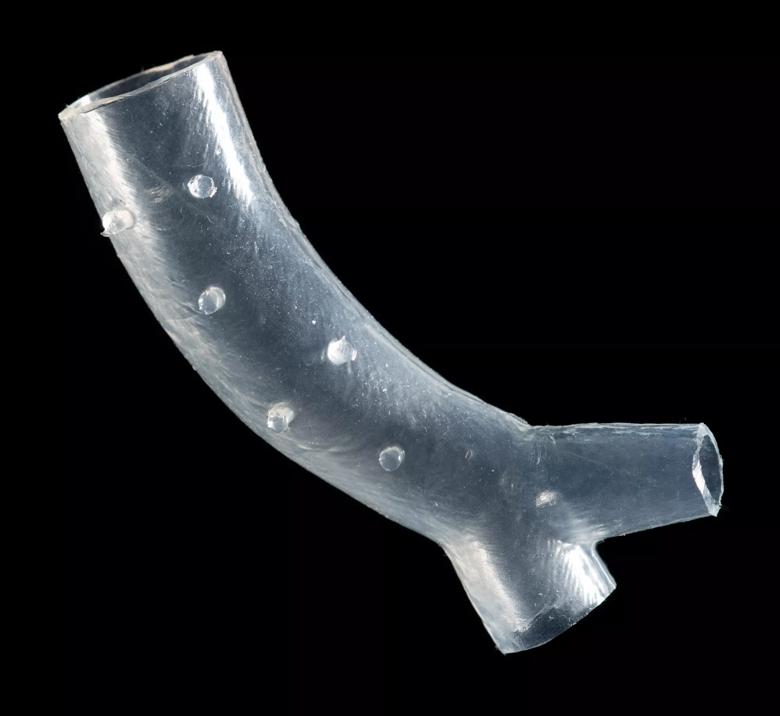
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/9638d8bb-4649-4b48-b4b1-18a53533a48e/lung-stent-CCM_1803068_12-27-19_006_DG-crop_jpg)
An example of a patient-specific airway stent developed at Cleveland Clinic.
It’s estimated that about 30,000 airway stents will be implanted in the U.S. in 2020.
Patient-specific products manufactured with 3D printing, including the airway stents, were named as one of the top 10 innovations at Cleveland Clinic’s annual Medical Innovations Summit in 2018. Dr. Gildea was also the recipient of the Outstanding Innovation in Medical Device award at the 2018 annual Inventor Awards Reception held by Cleveland Clinic Innovations.
With personalized medical devices more common in orthopedics, the patient-specific stent was developed and FDA cleared by an engineering team inside an orthopedic-focused Cleveland Clinic subsidiary. A new subsidiary named VisionAir Solutions will be formed around the technology with the sole mission of bringing more personalized medical devices to interventional pulmonologists and the patients who need them. By the end of the first quarter of 2020, this new spin-off company plans to begin providing the personalized stents to patients in a controlled launch at many of the country’s top medical institutions.
Dr. Gildea is an inventor of this technology that is being manufactured by a Cleveland Clinic spin-off company. Dr. Gildea and Cleveland Clinic may benefit financially if the technology is successful.
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit multispecialty academic medical center that integrates clinical and hospital care with research and education. Located in Cleveland, Ohio, it was founded in 1921 by four renowned physicians with a vision of providing outstanding patient care based upon the principles of cooperation, compassion and innovation. Cleveland Clinic has pioneered many medical breakthroughs, including coronary artery bypass surgery and the first face transplant in the United States. Cleveland Clinic is consistently recognized in the U.S. and throughout the world for its expertise and care. Among Cleveland Clinic’s 82,600 employees worldwide are more than 5,786 salaried physicians and researchers, and 20,700 registered nurses and advanced practice providers, representing 140 medical specialties and subspecialties. Cleveland Clinic is a 6,728-bed health system that includes a 173-acre main campus near downtown Cleveland, 23 hospitals, 280 outpatient facilities, including locations in northeast Ohio; Florida; Las Vegas, Nevada; Toronto, Canada; Abu Dhabi, UAE; and London, England. In 2024, there were 15.7 million outpatient encounters, 333,000 hospital admissions and observations, and 320,000 surgeries and procedures throughout Cleveland Clinic’s health system. Patients came for treatment from every state and 112 countries. Visit us at clevelandclinic.org. Follow us at x.com/CleClinicNews. News and resources are available at newsroom.clevelandclinic.org.
Editor’s Note: Cleveland Clinic News Service is available to provide broadcast-quality interviews and B-roll upon request.